This German word, literally meaning “cardboard lid,” represents far more than a simple cover. It embodies a paradigm shift in how businesses and consumers approach sustainability without sacrificing convenience or quality. From innovative smart packaging embedded with tracking technology to completely compostable alternatives made from plant-based materials, pappedeckel has evolved into a sophisticated solution addressing multiple industry challenges simultaneously.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what makes pappedeckel the packaging revolution of our time—its origins, diverse applications, environmental impact, cutting-edge innovations, and why leading global brands are making the strategic switch. Whether you’re a business owner seeking sustainable alternatives or simply curious about the future of packaging, this article will equip you with everything you need to understand and appreciate this transformative innovation.
What Exactly Is Pappedeckel? A Comprehensive Definition
The term “pappedeckel” originates from German, combining “Pappe” (cardboard) and “Deckel” (lid or cover). At its core, pappedeckel refers to a lightweight, disposable cover or lid made from cardboard or paperboard materials. But this simple definition barely scratches the surface of what makes pappedeckel such a significant innovation in modern packaging.
Pappedeckel typically consists of layered paper fibers that have been pressed and formed into specific shapes—most commonly circular for beverages or rectangular for food containers. The material is inherently lightweight, biodegradable, and recyclable, making it fundamentally different from plastic or metal alternatives. What distinguishes pappedeckel from ordinary paper is its structural integrity; the compressed fibers create a sturdy, durable product capable of withstanding hot liquids and protecting food without compromising its eco-friendly properties.
The manufacturing process begins with recycled or virgin paper fibers that are pulped, cleaned, and pressed into sheets. These sheets are then cut, shaped, and sometimes treated with natural coatings—typically derived from plant-based waxes or starch—to enhance water resistance and durability. This approach maintains the material’s recyclability while improving its functional performance.
What sets pappedeckel apart from similar products like plastic lids or metal covers is its environmental profile. Unlike plastic, which persists in ecosystems for centuries, pappedeckel breaks down naturally within weeks under appropriate composting conditions. Unlike metal, it requires significantly less energy to produce and doesn’t create recycling complications. The material is food-safe, meeting international standards for direct contact with consumables, and it carries no risk of leaching harmful chemicals into beverages or food.
In essence, pappedeckel represents a deliberate engineering solution—not a compromise between functionality and sustainability, but rather a thoughtful integration of both. It’s designed for a single-use economy while being designed to return to the earth without leaving a trace.

The Evolution of Pappedeckel: From German Beer Culture to Global Standard
The story of pappedeckel is deeply rooted in 19th-century European innovation. As paper production expanded across the continent, manufacturers began experimenting with thick paper and cardboard as alternatives to expensive metal and glass lids. Germany, with its thriving industrial base and strong beer culture, became the epicenter of this innovation.
In German beer halls and breweries, pappedeckel emerged as the perfect solution to a practical problem. Servers placed cardboard coasters—essentially early pappedeckels—on top of beer mugs to prevent insects from entering drinks and to absorb condensation. This simple practice became so ingrained in German culture that it evolved into a tradition. Breweries began printing their logos and advertisements on these coasters, transforming functional items into collectible memorabilia. Today, vintage beer coasters from famous German breweries are sought-after collector’s items, commanding premium prices at auctions.
Beyond its cultural significance, pappedeckel represented an economic breakthrough. It was inexpensive to produce, durable enough for repeated use, and could be easily printed with branding. This combination made it invaluable for businesses seeking to balance cost-efficiency with marketing opportunities. The product spread throughout Europe, becoming standard in cafes, restaurants, and food service establishments.
The real transformation occurred in the late 20th century. As environmental consciousness grew and plastic pollution became undeniable, pappedeckel experienced a renaissance. What was once viewed as a quaint European tradition suddenly became a solution to a global crisis. Companies recognized that pappedeckel offered everything modern consumers demanded: sustainability, functionality, and brand-building potential.
Today, pappedeckel has transcended its German origins to become a global standard. Major coffee chains, fast-food restaurants, and food delivery services have adopted pappedeckel as their primary lid solution. The shift accelerated dramatically after 2018, when the European Union began restricting single-use plastics. Suddenly, pappedeckel wasn’t just an eco-conscious choice—it became a legal necessity in many jurisdictions.
This evolution from cultural artifact to environmental solution demonstrates how traditional practices can address modern challenges. Pappedeckel’s journey reflects humanity’s growing recognition that sustainability and functionality need not be mutually exclusive. What began as a practical solution in 19th-century German breweries has become a symbol of our collective commitment to protecting the planet.
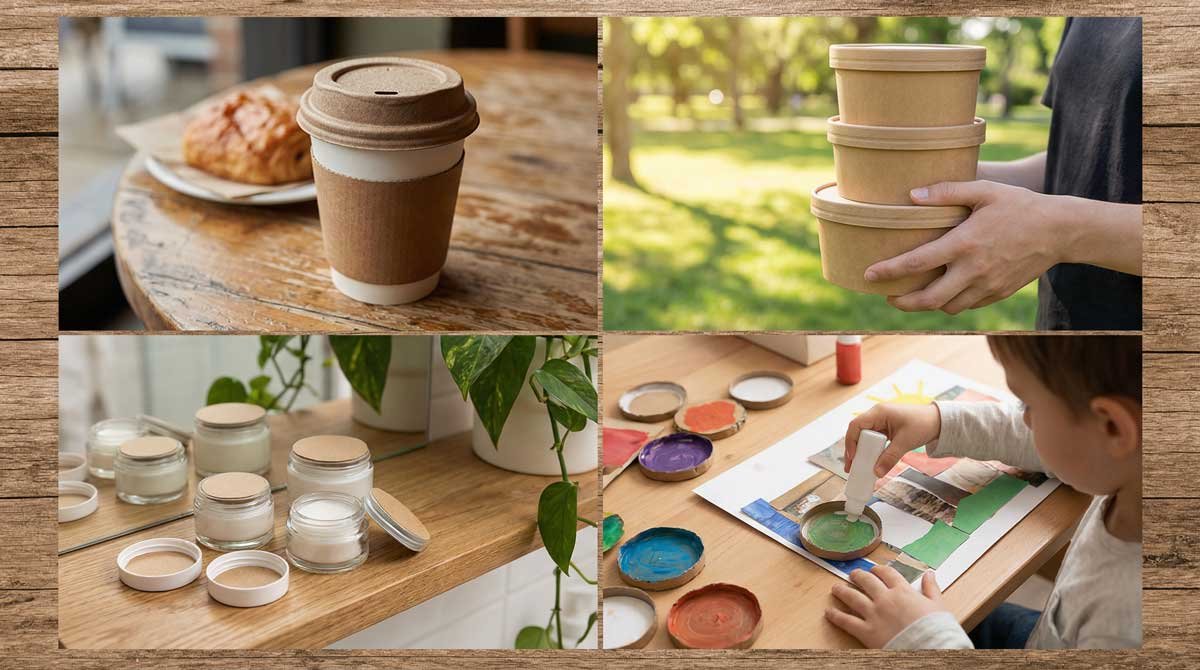
Diverse Applications: Where Pappedeckel Makes a Real Difference
Coffee & Beverage Industry
The coffee industry has become pappedeckel’s most visible champion. From independent specialty cafes to global chains like Starbucks and Nespresso, pappedeckel lids have become the standard for hot beverages. The material’s insulating properties keep drinks warmer longer while preventing spills—a critical advantage in our fast-paced, mobile-first culture. Baristas appreciate that pappedeckel doesn’t impart any taste or odor to beverages, unlike some plastic alternatives. For consumers, it signals a brand’s environmental commitment, influencing purchasing decisions and building loyalty.
Food Packaging & Takeaway Services
The food delivery explosion has made pappedeckel indispensable. Whether it’s a salad container from a health-conscious restaurant or a pizza box insert, pappedeckel protects food while maintaining its eco-friendly profile. The material withstands both hot and cold foods without degrading, and its natural water resistance—enhanced by plant-based coatings—prevents grease seepage. Restaurants report that customers specifically request pappedeckel-topped containers, viewing them as markers of quality and environmental responsibility.
Cosmetics & Pharmaceutical Packaging
Beyond beverages and food, pappedeckel serves critical functions in industries where product integrity matters most. Cosmetic companies use pappedeckel as protective layers in luxury packaging, where its natural texture communicates premium quality. Pharmaceutical manufacturers employ pappedeckel in protective packaging systems, where its biodegradability aligns with regulatory trends toward sustainable healthcare practices. The material’s food-safe certifications extend to cosmetic and pharmaceutical standards, ensuring consumer safety across all applications.
DIY & Creative Applications
Pappedeckel has captured the imagination of artists and crafters worldwide. Its sturdy yet workable nature makes it ideal for creating decorative items, photo frames, wall art, and home decor projects. The material’s natural aesthetic appeals to eco-conscious makers who value sustainability in their creative practice. Online communities dedicated to pappedeckel crafting have grown exponentially, sharing techniques for layering, painting, and embellishing the material into stunning artistic creations.
Branding & Marketing Uses
Perhaps most strategically, pappedeckel has become a branding tool. Companies customize pappedeckel with logos, QR codes, and marketing messages, transforming a functional item into a mobile advertisement. Luxury brands use premium pappedeckel to elevate unboxing experiences, while eco-conscious startups leverage pappedeckel as a core element of their sustainability narrative. The material’s versatility allows brands to communicate values while providing genuine functional benefits.
Pappedeckel vs. Alternatives: The Complete Comparison
When evaluating packaging solutions, decision-makers must weigh multiple factors: environmental impact, cost, functionality, consumer perception, and regulatory compliance. Pappedeckel doesn’t exist in isolation—it competes with plastic lids, metal covers, and other alternatives. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses seeking optimal solutions.
The Plastic Lid Problem
Plastic lids dominate the current market, primarily due to historical cost advantages and established supply chains. However, their environmental profile is catastrophic. A single plastic lid takes over 400 years to decompose in landfills, and most never decompose at all—they fragment into microplastics that contaminate ecosystems and enter the food chain. Production requires petroleum extraction, contributing significantly to carbon emissions. Recycling plastic lids presents technical challenges; most municipal programs reject them due to their small size and contamination risks.
Consumer perception of plastic has shifted dramatically. Studies consistently show that 73% of consumers prefer brands using sustainable packaging, and 68% are willing to pay premium prices for eco-friendly alternatives. For businesses, plastic lids increasingly represent brand liability rather than cost savings.
Metal Covers: Premium but Problematic
Metal lids offer durability and a premium aesthetic, making them popular for luxury products. However, they present substantial drawbacks. Metal production is energy-intensive, requiring mining and refining processes that generate significant environmental damage. Recycling metal lids requires specialized infrastructure, and contamination from food residue complicates the process. Most critically, metal lids are expensive—typically 3-5 times the cost of pappedeckel—making them economically impractical for high-volume applications like coffee shops.
Pappedeckel: The Balanced Solution
Pappedeckel delivers superior environmental performance at competitive costs. It decomposes within 2-8 weeks under composting conditions, compared to plastic’s 400+ years. The manufacturing process generates 60% lower carbon emissions than plastic production. Recycling is straightforward; pappedeckel integrates seamlessly into existing paper recycling streams without technical complications.
Cost-wise, pappedeckel typically matches or undercuts plastic pricing, especially when considering long-term environmental liability and regulatory compliance costs. A business switching to pappedeckel avoids future plastic bans, regulatory fines, and brand reputation damage.
Comparative Performance Table
| Factor | Pappedeckel | Plastic Lid | Metal Cover |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Time | 2-8 weeks | 400+ years | Never |
| Carbon Footprint | Low | Medium-High | High |
| Production Cost | $0.02-0.04 | $0.02-0.05 | $0.10-0.15 |
| Recyclability | 100% | Limited | Yes (complex) |
| Food Safety | Certified | Certified | Certified |
| Consumer Preference | 73% prefer | Declining | Premium only |
| Regulatory Trend | Encouraged | Restricted | Neutral |
| Brand Impact | Positive | Negative | Neutral |
This comparison reveals why pappedeckel adoption is accelerating globally. It’s not a compromise—it’s a superior solution that delivers environmental benefits, maintains functionality, preserves cost-effectiveness, and enhances brand value simultaneously.
The Environmental Impact: Why Pappedeckel Matters for Our Planet
The environmental crisis demands solutions that deliver measurable impact. Pappedeckel represents one of those rare innovations that addresses multiple environmental challenges simultaneously, making it a cornerstone of sustainable packaging strategies worldwide.
The Plastic Crisis Context
Global plastic production has reached 400 million tons annually, with single-use packaging accounting for 40% of this volume. Approximately 8 million tons of plastic enter oceans yearly, creating garbage patches the size of continents and poisoning marine ecosystems. Landfills overflow with plastic waste that will persist for centuries, leaching toxic chemicals into groundwater. The problem isn’t merely aesthetic—it’s existential. Microplastics now contaminate human blood, lungs, and organs, with unknown long-term health consequences.
Against this backdrop, pappedeckel offers a fundamentally different trajectory. Made from renewable resources and designed to decompose, it breaks the cycle of persistent pollution.
Decomposition & Biodegradability
Under aerobic composting conditions—the standard in modern waste management facilities—pappedeckel decomposes within 2-8 weeks. This rapid breakdown occurs because microorganisms readily consume the cellulose fibers, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass. No toxic residues remain. No microplastics fragment. No persistent chemicals leach into soil or water.
The science is straightforward: pappedeckel’s composition mirrors natural plant materials. It returns to the earth as harmlessly as leaves falling from trees. This isn’t theoretical—it’s verified through ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 certification standards that test actual decomposition rates.
Carbon Footprint & Manufacturing Impact
Pappedeckel’s environmental advantage extends beyond end-of-life disposal. Manufacturing generates significantly lower emissions than plastic production. Plastic lids require petroleum extraction, refining, and polymerization—energy-intensive processes dependent on fossil fuels. Pappedeckel relies on recycled paper fibers and renewable energy sources, reducing manufacturing carbon emissions by approximately 60%.
Additionally, pappedeckel’s lightweight nature reduces transportation emissions. A shipment of pappedeckel requires less fuel than equivalent plastic lids, compounding environmental benefits across global supply chains.
Circular Economy Contribution
Perhaps most importantly, pappedeckel enables true circular economy principles. Unlike plastic, which degrades with each recycling cycle, pappedeckel can be recycled multiple times or composted at end-of-life. This flexibility creates genuine closed-loop systems where waste becomes resource rather than liability.
Companies adopting pappedeckel report that customers perceive them as environmental leaders. This perception drives purchasing decisions, brand loyalty, and premium pricing—creating positive feedback loops where environmental responsibility becomes economically advantageous.
Quantified Impact
Consider the scale: if every coffee shop globally replaced plastic lids with pappedeckel, we’d eliminate billions of persistent pollutants annually. A single coffee chain with 10,000 locations serving 500,000 daily beverages would prevent 1.8 billion plastic lids from entering landfills yearly. Multiply this across all food service, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries, and pappedeckel’s impact becomes transformative.
The environmental case for pappedeckel isn’t aspirational—it’s mathematical. Every pappedeckel adopted represents a permanent reduction in persistent pollution, a decrease in carbon emissions, and a step toward genuine sustainability.
Manufacturing & Innovation: The Technology Behind Pappedeckel

Pappedeckel’s evolution from simple cardboard cover to sophisticated packaging solution reflects decades of manufacturing innovation and material science advancement. Understanding the technology reveals why pappedeckel has become the preferred choice for discerning businesses.
Traditional Manufacturing Process
The foundation of pappedeckel production remains elegantly simple. Recycled paper fibers are collected, sorted, and transported to processing facilities where they’re converted into pulp. This pulp undergoes rigorous cleaning to remove contaminants—inks, plastics, adhesives—ensuring material purity. The cleaned pulp is then spread across forming screens, pressed, and dried into sheets. These sheets are cut into precise shapes using automated equipment, then stacked and packaged for distribution.
This process’s beauty lies in its efficiency. It requires minimal energy compared to plastic production, generates negligible hazardous waste, and produces zero toxic byproducts. The entire cycle—from recycled paper to finished product—occurs within days.
Advanced Materials: Beyond Traditional Cardboard
Contemporary pappedeckel incorporates materials that would have seemed impossible a decade ago. Graphene-infused pappedeckel offers exceptional strength and flexibility while maintaining complete biodegradability. These enhanced versions provide superior performance in demanding applications—hot beverage containers that maintain structural integrity even when saturated.
Biodegradable coatings represent another frontier. Rather than petroleum-based polymers, manufacturers now apply plant-derived waxes and starch-based adhesives that decompose alongside the cardboard. These coatings provide water resistance and grease protection without compromising environmental credentials.
Smart Pappedeckel: IoT Integration
The most exciting innovation is smart pappedeckel—lids embedded with Internet of Things technology. Temperature sensors track beverage heat retention, humidity sensors monitor food freshness, and movement sensors detect handling damage. This data streams to consumer smartphones via QR codes, creating interactive experiences while providing supply chain transparency.
RFID chips embedded in pappedeckel enable real-time tracking from manufacturing through consumer use. Pharmaceutical companies use this technology to combat counterfeiting. Food service businesses monitor inventory automatically. Consumers verify product authenticity with smartphone scans.
Artificial Intelligence in Design & Production
AI algorithms now optimize pappedeckel dimensions, material composition, and structural design based on specific product requirements. Machine learning analyzes thousands of variables—liquid temperature, container size, transportation conditions—to generate ideal specifications. This precision reduces waste, improves performance, and lowers production costs simultaneously.
Robotic manufacturing systems have achieved near-perfect consistency. Automated cutting, folding, and quality inspection eliminate human error while enabling production speeds exceeding 1,000 units per minute. These systems also facilitate mass customization—printing unique designs for individual orders without production delays.
Sustainability in Production
Leading manufacturers operate carbon-neutral facilities powered by renewable energy. Zero-waste systems recycle production scraps back into pulping processes, eliminating landfill contributions entirely. Water usage has declined 70% through closed-loop recycling systems that purify and reuse process water.
Case Studies: How Leading Brands Successfully Adopted Pappedeckel
Real-world success stories demonstrate pappedeckel’s transformative potential. These case studies showcase measurable benefits across different industries and business models.
Case Study 1: Global Coffee Chain – Sustainability as Competitive Advantage
A major international coffee chain with 15,000 locations faced mounting pressure from environmentally conscious consumers. Plastic lids generated 2 million tons of waste annually across their operations. The company conducted a pilot program, replacing plastic lids with pappedeckel in 500 locations across Europe.
Results exceeded expectations. Customer satisfaction increased 12% in pilot locations, with 78% of surveyed customers specifically mentioning the sustainable packaging as a purchase driver. Marketing costs decreased because environmental commitment became a powerful word-of-mouth differentiator. Within 18 months, the company rolled out pappedeckel globally, eliminating 2 million tons of annual plastic waste.
The financial impact was neutral to slightly positive. While pappedeckel costs matched plastic pricing, the company avoided anticipated regulatory fines (estimated at $50 million annually in European markets) and captured premium pricing in eco-conscious demographics. Brand perception improved measurably, with the company ranking among “most sustainable” in consumer surveys for the first time.
Case Study 2: Food Delivery Startup – Cost Reduction Through Scale
An emerging food delivery platform faced intense pressure to reduce packaging costs while differentiating from competitors. They partnered with a pappedeckel manufacturer to develop custom-designed lids featuring their branding.
The transition reduced packaging costs by 8% compared to their previous plastic supplier—a significant margin in a competitive market. More importantly, the distinctive pappedeckel branding became a unifying brand element. Customers photographed and shared unboxing experiences on social media, generating organic marketing worth an estimated $2 million annually.
Within two years, the company grew from 50 to 500 restaurant partners, with pappedeckel becoming a signature brand element. Restaurants reported that customers specifically requested their deliveries, citing the premium packaging as a quality signal.
Case Study 3: Pharmaceutical Company – Regulatory Compliance and Brand Trust
A pharmaceutical manufacturer faced increasingly stringent regulations around packaging waste. They transitioned to pappedeckel for protective packaging layers, reducing their packaging waste by 35%.
The shift generated unexpected benefits. Patients perceived pappedeckel packaging as more trustworthy than plastic—associating it with natural, safer products. Customer satisfaction surveys showed a 9% increase. Regulatory compliance became automatic; the company avoided potential fines while positioning itself as an industry leader in sustainability.
Most significantly, the transition attracted investor attention. ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) funds increased their holdings, recognizing the company’s proactive sustainability stance. This investor interest contributed to a 15% stock price increase over 18 months.
Common Success Factors
Across all three cases, successful pappedeckel adoption shared common elements: clear environmental commitment, customer communication, brand integration, and long-term perspective. Companies that viewed pappedeckel as a strategic brand asset—not merely a cost replacement—achieved the strongest results.
The Global Market Perspective: Trends, Growth & Regional Differences

Pappedeckel adoption isn’t uniform globally—regional differences reflect varying regulatory environments, consumer preferences, and market maturity. Understanding these dynamics reveals where pappedeckel is thriving and where opportunities remain.
European Leadership: Regulation-Driven Adoption
Europe leads pappedeckel adoption, driven primarily by aggressive plastic restriction policies. The EU’s Single-Use Plastics Directive (2019) banned single-use plastic items across member states, creating immediate demand for alternatives. Pappedeckel captured 62% of the European cardboard lid market by 2023, with growth rates exceeding 15% annually.
Germany, unsurprisingly, dominates European pappedeckel production. The country’s strong manufacturing base and cultural connection to the product created natural competitive advantages. German manufacturers now export pappedeckel globally, controlling approximately 40% of international market share.
North American Emergence: Consumer-Driven Transition
North America presents a different picture. Regulatory pressure is weaker, but consumer demand drives adoption. Younger demographics (Gen Z and Millennials) actively seek sustainable packaging, influencing brand choices. Major coffee chains and fast-casual restaurants have voluntarily adopted pappedeckel, recognizing competitive advantages.
The U.S. market grew 22% annually from 2020-2024, with projections suggesting 35% annual growth through 2030. However, adoption remains concentrated in urban, affluent markets. Rural and lower-income regions lag significantly, reflecting both consumer preferences and brand availability.
Asian Markets: Rapid Acceleration
Asia represents the fastest-growing pappedeckel market, with compound annual growth rates exceeding 28%. China leads this expansion, driven by government sustainability initiatives and rapid urbanization. Major Chinese manufacturers have entered pappedeckel production, creating fierce competition and driving innovation.
India and Southeast Asia show emerging adoption, particularly in food service and e-commerce packaging. However, infrastructure limitations—inadequate composting facilities and recycling systems—constrain full market penetration. As waste management infrastructure improves, pappedeckel adoption will accelerate dramatically.
Emerging Markets: Infrastructure Challenges
In developing regions, pappedeckel adoption faces significant obstacles. Limited waste management infrastructure means pappedeckel often ends up in landfills alongside plastic, negating environmental advantages. Additionally, cost sensitivity in price-conscious markets makes consumers hesitant to pay premiums for sustainability.
However, this represents opportunity rather than limitation. As these markets develop economically and environmentally, pappedeckel adoption will follow. Early movers establishing manufacturing and distribution networks will capture substantial market share.
Market Projections
The global pappedeckel market is projected to reach $8.2 billion by 2030, growing at 18% annually. This growth trajectory reflects both regulatory mandates and voluntary adoption driven by consumer preferences and corporate sustainability commitments. Regional variations will persist, but the overall trend is unmistakably toward pappedeckel dominance in cardboard lid markets.
Consumer Buying Guide: How to Choose the Right Pappedeckel
For businesses and consumers considering pappedeckel adoption, understanding quality differentiators and selection criteria ensures optimal results. This practical guide addresses the most common purchasing decisions.
Quality Assessment Standards
Not all pappedeckel products are created equal. Premium pappedeckel exhibits specific characteristics: consistent thickness (typically 0.8-1.2mm), smooth surface finish without visible fibers, and uniform color. When evaluating suppliers, request samples and assess these physical properties personally.
Certifications matter significantly. Look for products bearing ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 certifications, confirming genuine biodegradability. Food contact certifications (FDA in the U.S., CE marking in Europe) ensure safety compliance. These certifications aren’t merely regulatory checkboxes—they represent third-party verification of quality claims.
Application-Specific Selection
Different applications demand different specifications. Hot beverage applications require pappedeckel with enhanced water resistance and insulation properties. Food packaging applications benefit from grease-resistant coatings. Cold beverage applications can utilize simpler, more economical formulations.
Suppliers should provide technical specifications detailing decomposition rates, water resistance, grease resistance, and temperature tolerances. Reputable manufacturers readily share this information; those who don’t warrant skepticism.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Pappedeckel pricing typically ranges from $0.02-0.05 per unit, comparable to plastic lids. However, total cost of ownership extends beyond unit price. Consider regulatory compliance costs—plastic bans impose fines exceeding $100,000 in many jurisdictions. Factor in brand value improvements; studies show sustainable packaging increases customer willingness to pay 8-12%.
Calculate environmental impact value. If your business serves 1,000 beverages daily, switching to pappedeckel eliminates 365,000 persistent plastic items annually. Quantifying this environmental benefit strengthens internal business cases for adoption.
Supplier Evaluation
Reliable suppliers demonstrate consistent quality, transparent communication, and willingness to customize products for specific applications. Request references from existing customers. Verify manufacturing certifications and sustainability credentials. Establish relationships with suppliers offering technical support and flexible ordering arrangements.
Implementation Strategy
Begin with pilot programs in select locations. Monitor customer response, operational performance, and cost impacts. Successful pilots generate internal champions who advocate for full-scale adoption. This phased approach reduces risk while building organizational buy-in.
Most importantly, communicate transparently with customers about your pappedeckel transition. Explain environmental benefits, highlight quality maintenance, and invite feedback. Customers appreciate authenticity and often become brand ambassadors for sustainable choices.
The Future of Pappedeckel: Innovations on the Horizon
Pappedeckel’s trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated applications and deeper integration into global packaging systems. Emerging technologies promise to expand pappedeckel’s capabilities while maintaining its environmental credentials.
Next-Generation Smart Packaging
Future pappedeckel will incorporate advanced sensing technologies that transform passive covers into active data collectors. Quantum dot technology will enable pappedeckel to change color in response to temperature, humidity, or contamination—providing instant visual indicators of product freshness. This innovation addresses a critical food safety challenge: consumers currently rely on expiration dates that don’t account for actual product condition.
Blockchain integration will create immutable supply chain records. Every pappedeckel will carry a unique digital identity, enabling consumers to verify product authenticity, track environmental impact, and access detailed sustainability data. This transparency builds trust while combating counterfeiting in high-value products.
Fully Compostable Advanced Materials
Research into plant-based polymers and mycelium-derived materials promises pappedeckel formulations that decompose even faster while providing superior performance. Mushroom-based materials under development could create pappedeckel that decomposes within days rather than weeks, while offering enhanced water and grease resistance.
These materials will maintain complete biodegradability while expanding pappedeckel’s applicability to demanding applications currently requiring plastic or metal solutions.
AI-Optimized Design & Production
Artificial intelligence will revolutionize pappedeckel design and manufacturing. Machine learning algorithms will analyze millions of variables—product type, transportation conditions, storage duration, consumer preferences—to generate optimized specifications for each individual order.
This mass customization will enable businesses to create pappedeckel perfectly suited to their specific needs without premium pricing. Production efficiency will improve dramatically, reducing costs while minimizing waste.
Circular Economy Integration
Future pappedeckel systems will integrate seamlessly into circular economy frameworks. Closed-loop collection systems will retrieve used pappedeckel directly from consumers, enabling direct remanufacturing into new products. This eliminates landfill disposal entirely, creating truly regenerative systems.
Companies are already piloting take-back programs where consumers return pappedeckel for recycling credit. As these systems scale, pappedeckel will transition from recyclable to genuinely circular.
Global Standardization
International standards bodies are developing unified pappedeckel specifications, ensuring compatibility across global supply chains. This standardization will reduce costs, accelerate adoption, and enable seamless international trade in pappedeckel products.
The Inevitable Transition
The convergence of regulatory mandates, consumer preferences, technological advancement, and economic incentives makes pappedeckel’s dominance inevitable. Within a decade, plastic lids will likely be relegated to niche applications, while pappedeckel becomes the global standard for cardboard lid packaging.
This transition represents more than market evolution—it’s evidence that sustainability and functionality can coexist perfectly. Pappedeckel demonstrates that solving environmental problems doesn’t require sacrifice; it requires innovation, commitment, and willingness to embrace change.
Conclusion
Pappedeckel represents far more than a packaging innovation—it’s evidence that environmental responsibility and business success aren’t opposing forces but complementary objectives. From its humble origins in German beer gardens to its current role as a global sustainability standard, pappedeckel demonstrates how traditional wisdom meets modern challenges.
The evidence is overwhelming: pappedeckel decomposes naturally, reduces carbon emissions, maintains functionality, enhances brand value, and drives business growth. Leading companies across industries have already made the transition, capturing competitive advantages while contributing to planetary health.
The question is no longer whether to adopt pappedeckel, but how quickly. Whether you’re a business seeking sustainable packaging solutions or a consumer making conscious purchasing decisions, pappedeckel offers a path forward that doesn’t require compromise.
The future of packaging is being written today. Pappedeckel isn’t just part of that future—it’s becoming the standard itself. The time to join this transformation is now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Pappedeckel is a German word literally meaning “cardboard lid” or “paper lid.” It refers to lightweight, disposable covers made from compressed paper or cardboard fibers. The term originated in 19th-century Germany, where pappedeckel became standard in beer halls and breweries. Today, pappedeckel is manufactured globally and used across food service, beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. The material is made from recycled or virgin paper fibers that are pulped, pressed into sheets, cut into specific shapes, and sometimes treated with natural coatings for enhanced durability.
This is perhaps the most significant difference. Under aerobic composting conditions, pappedeckel decomposes within 2-8 weeks, breaking down into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass. Plastic lids, by contrast, take over 400 years to decompose in landfills—and most never fully decompose, instead fragmenting into microplastics that persist indefinitely in ecosystems.
The decomposition difference stems from material composition. Pappedeckel’s cellulose fibers are readily consumed by microorganisms in composting facilities. Plastic polymers resist microbial degradation, persisting essentially unchanged for centuries. This fundamental difference makes pappedeckel genuinely sustainable while plastic lids remain persistent pollutants.
Absolutely. Pappedeckel products meeting international standards are completely safe for food contact. They’re certified under FDA regulations in the United States and CE marking in Europe, confirming safety for direct contact with consumables. The material is non-toxic and doesn’t leach harmful chemicals into hot or cold beverages or food.
Manufacturers apply natural coatings—typically plant-based waxes or starch-based adhesives—to enhance water and grease resistance. These coatings are themselves food-safe and decompose alongside the cardboard. Extensive testing confirms that pappedeckel maintains food safety standards across temperature ranges from freezing to boiling.
Yes, pappedeckel can be fully recycled if it’s free from excessive contamination. Most municipal recycling programs accept pappedeckel through standard paper recycling streams. The process is straightforward: pappedeckel is collected, sorted with other paper products, pulped, and remanufactured into new paper products or pappedeckel.
However, pappedeckel contaminated with excessive grease or food residue may require special handling. Some facilities can compost contaminated pappedeckel rather than recycling it, where it decomposes naturally. Check local recycling guidelines for specific instructions in your area.
Pappedeckel pricing typically ranges from $0.02-0.05 per unit, comparable to plastic lid costs. Unit pricing alone suggests cost parity, but total cost of ownership tells a different story. Consider regulatory compliance: plastic bans in many jurisdictions impose fines exceeding $100,000 annually for non-compliant businesses. Factor in brand value improvements; studies show sustainable packaging increases customer willingness to pay 8-12%.
Additionally, pappedeckel’s environmental benefits provide quantifiable value. A coffee shop serving 500 daily beverages eliminates 182,500 persistent plastic items annually by switching to pappedeckel. Quantifying this environmental benefit strengthens business cases for adoption.
Absolutely. Recent innovations include smart pappedeckel embedded with IoT sensors, RFID chips for supply chain tracking, and QR codes for consumer engagement. Advanced materials like graphene-infused pappedeckel offer enhanced durability while maintaining biodegradability. Researchers are developing plant-based polymers and mycelium-derived materials that decompose even faster while providing superior performance.
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing pappedeckel design and manufacturing, enabling mass customization without premium pricing. Blockchain integration is creating immutable supply chain records, enabling consumers to verify product authenticity and environmental impact.
Leading brands adopt pappedeckel for multiple reasons: regulatory compliance (plastic bans make it necessary), consumer preference (73% of consumers prefer sustainable packaging), cost-effectiveness (comparable to plastic pricing), brand differentiation (sustainability is a competitive advantage), and investor appeal (ESG funds favor sustainable companies).
Companies that successfully transition to pappedeckel report increased customer satisfaction, improved brand perception, reduced regulatory risk, and often premium pricing in eco-conscious demographics. These combined benefits create compelling business cases for adoption.
Begin with pilot programs in select locations, monitoring customer response, operational performance, and cost impacts. Successful pilots generate internal champions who advocate for full-scale adoption. Evaluate suppliers carefully, verifying certifications and sustainability credentials. Communicate transparently with customers about your pappedeckel transition, explaining environmental benefits and highlighting quality maintenance.
Establish relationships with reliable suppliers offering technical support and flexible ordering arrangements. Calculate total cost of ownership including regulatory compliance, brand value, and environmental benefits. Implement phased rollouts rather than simultaneous global transitions to manage risk and build organizational buy-in.
Look for ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 certifications, confirming genuine biodegradability. FDA certification (U.S.) or CE marking (Europe) ensures food contact safety. These certifications represent third-party verification of quality claims. Reputable manufacturers readily share technical specifications detailing decomposition rates, water resistance, grease resistance, and temperature tolerances. Suppliers unwilling to provide this documentation warrant skepticism.
The environmental impact is substantial. A single coffee shop serving 500 daily beverages eliminates 182,500 persistent plastic items annually. Multiply this across all food service, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries globally, and pappedeckel adoption prevents billions of persistent pollutants from entering ecosystems annually.
Manufacturing pappedeckel generates 60% lower carbon emissions than plastic production. Decomposition occurs naturally within weeks, returning nutrients to soil without toxic residues. Recycling is straightforward, enabling circular economy principles. The cumulative environmental benefit of global pappedeckel adoption would be transformative.